- About the author
- Questions and Issues
- Edit and Contribute
- Introduction
- 1. What is a sensor?
- 2. Types of sensors
- 3. Android Sensors API
- 4. Sensor Rates
- 5. Raw Sensors and Composite Sensors
- 6. Sensor Coordinate System
- 7. Accelerometer
- 8. Gravity and Linear Acceleration
- 9. Best Practices
- 10. References
- 11. Examples
- Generated using GitBook
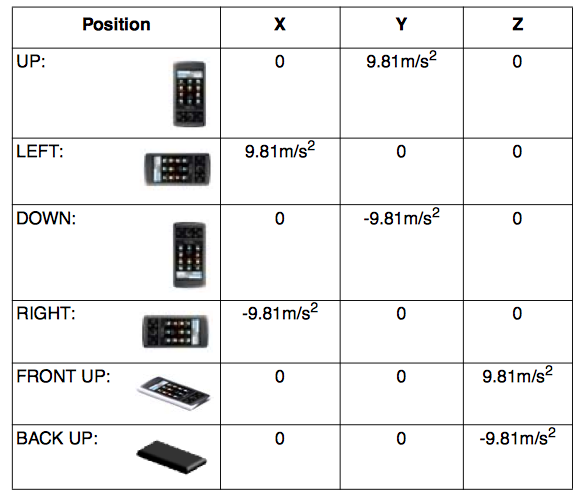
Accelerometer
Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER
| Type | Description | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware | Measures the acceleration force in m/s^2 that is applied to a device on all three physical axes (x, y, and z), including the force of gravity. | Motion detection (shake, tilt, etc.). |
Note that the readings from the accelerometer include the acceleration due to gravity (which is opposite to the direction of the gravity vector).
Examples:
- The norm of
<x, y, z>should be close to 0 when in free fall. - When the device lies flat on a table and is pushed on its left side toward the right, the x acceleration value is positive.
- When the device lies flat on a table, the acceleration value is +9.81, which correspond to the acceleration of the device (0 m/s^2) minus the force of gravity (-9.81 m/s^2).
- When the device lies flat on a table and is pushed toward the sky, the acceleration value is greater than +9.81, which correspond to the acceleration of the device (+A m/s^2) minus the force of gravity (-9.81 m/s^2).
Table 1: Acceleration Values on each Axis for Different Positions.